Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
It is increasingly evident that many metabolic
2024-04-26
It is increasingly evident that many metabolic genes are associated with cancer progression of various tumor cells, including NSCLC. In particular, GLUT1 overexpression has been reported in NSCLC, and correlations between GLUT1 expression and a number of clinical parameters such as gender, smoking s
-
br Introduction Rhamdia quelen jundi Silurifomes Heptapterid
2024-04-26
Introduction Rhamdia quelen (jundiá, Silurifomes, Heptapteridae) is a neotropical catfish widely distributed in Central and South America (Silfvergrip, 1996). This species shows high potential for the aquaculture industry, due to an elevated growth rate, good carcass yield, and easy reproduction
-
Although the exact mechanisms are
2024-04-26
Although the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, IGF-1 is tightly linked with ER and estrogen actions and a crosstalk occurs between these two systems in breast cancer. To illustrate this close relationship, studies have identified a synergy between IGF-1 and estrogen in Mifepristone synthesi
-
br Experimental Section br Results and
2024-04-26
Experimental Section Results and Discussion Conclusions The advantages of the novel enzymo-chemical method for Mn and Co assay are simplicity of analytical procedure and economic effect due to the usage of only one enzyme in the form of apo-enzyme. An effectiveness of the apo-arginase-based
-
Enhancers are short regions of DNA
2024-04-26
Enhancers are short regions of DNA that are bound by DNA-binding proteins (TFs) to increase the likelihood of a particular gene to be expressed. Importantly, enhancers can be identified, and classified, by their patterns of chromatin accessibility and of enrichment in certain histone modifications.
-
While we chose to divide our etiologies into three
2024-04-26
While we chose to divide our etiologies into three categories, it should be noted that such division has certain limitations. Even though URIs and the common cold are considered mainly viral in origin and rhinosinusitis mainly bacterial in origin,26, 27 there is considerable overlap between these co
-
Cellular detoxification is an important process
2024-04-26
Cellular detoxification is an important process that helps remove excess oxidants from the cellular environment through endogenous antioxidants or other molecules capable of reduction. One of the key regulators of antioxidant production is the transcription factor, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived
-
We recently identified a G A dependent
2024-04-25
We recently identified a G9A-dependent epigenetic mechanism for transcriptional activation of the serine pathway in cancer cells (Ding et al., 2013). G9A, also known as EHMT2 and KMT1C, is a H3K9 methyltransferase that has a primary role in catalyzing H3K9me1 and H3K9me2 in euchromatin (Shinkai and
-
This study demonstrates numerical alterations of creatinine
2024-04-25
This study demonstrates numerical alterations of creatinine levels potentially reflecting ongoing or even higher myocardial contraction of the LAA after successful LAAC. Creatinine is the direct breakdown product of creatine in muscle, the key metabolite for energy supply during muscular and myocard
-
The complex role of the human intestinal microbiota is emerg
2024-04-25
The complex role of the human intestinal microbiota is emerging and its functions has been elucidated when considering energy metabolism, nutrient digestion, vitamin synthesis, epithelial defenses and immune responses [34]. The colon is responsible for salvage of energy and possibly nitrogen from ca
-
In contrast to the beneficial treatment
2024-04-25
In contrast to the beneficial treatment of skin-inflammation with PAH containing coal tar, epidemiology showed that environmental pollution, containing AHR-activating PAH, lead to more eczema [80]. Of note, other epidemiological data suggested that Th17 cell polarization may be enhanced air pollutio
-
Diabetes or inflammation is associated with up regulation
2024-04-25
Diabetes or inflammation is associated with up-regulation of A2AAR (Pang et al., 2010). High levels of A2AARs are found in macrophages and microglial cells that are poised, on activation, to abrogate the immune response (Trincavelli et al., 2008). In addition, hyperglycemia is associated with increa
-
d-biotin australia br Funding br Introduction l Dihydroxyphe
2024-04-25
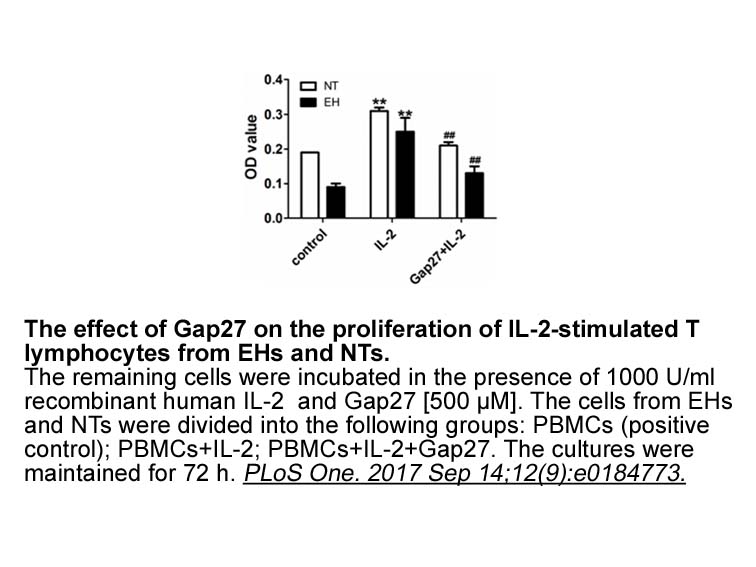
Funding Introduction l-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA) is the gold-standard treatment for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD); however, its chronic use induces severe motor complications that eventually limit its long-term efficacy (Bastide et al., 2015). The most disabling side
-
Although experiments on animals and cells indicate that anti
2024-04-25
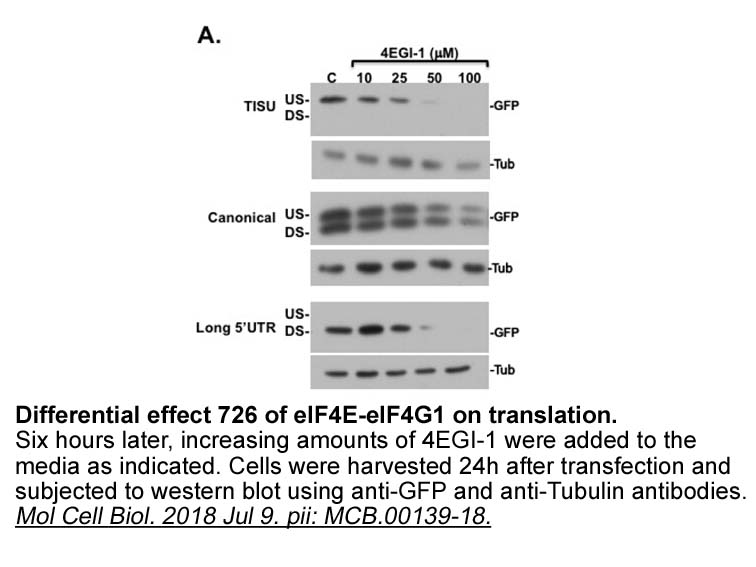
Although experiments on animals and cells indicate that antioxidant and free radical scavenging agents have protective effects against brain damage, the results of preclinical trials are not as encouraging. Edaravone is a type of free radical scavenging drug that was first used as a neuroprotective
-
Given the profound expression of HT A and HT A
2024-04-25
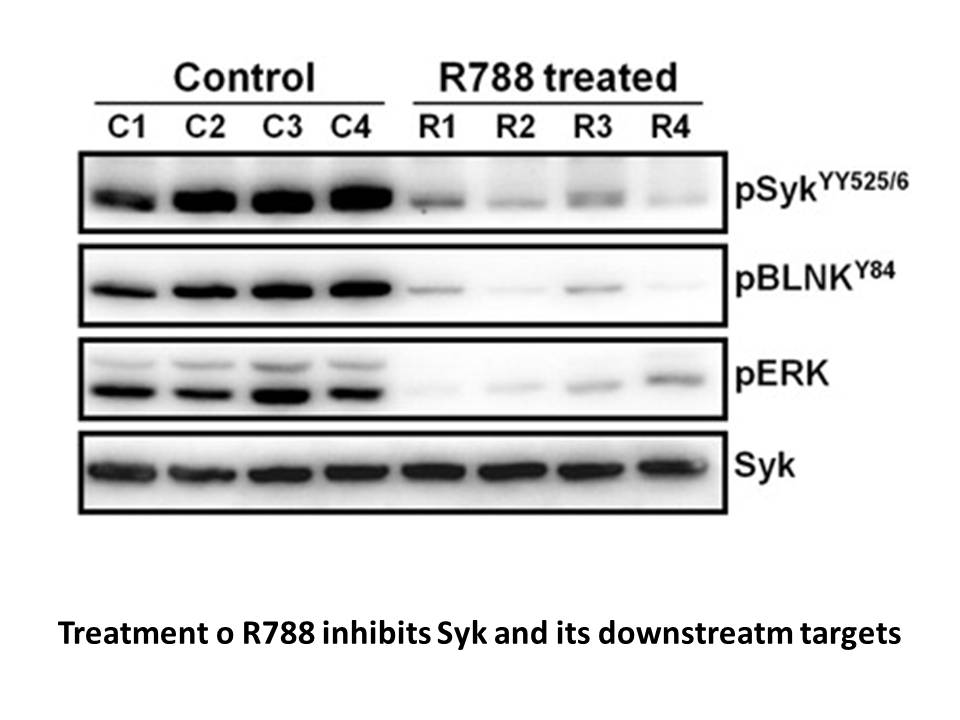
Given the profound Cy3 maleimide (non-sulfonated) of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A in the hippocampal CA1 region, and their potential to complex with mGluRs, the objective of this study was to examine if sleep deprivation alters the expression of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors and determine whether potential chang
16050 records 170/1070 page Previous Next First page 上5页 166167168169170 下5页 Last page